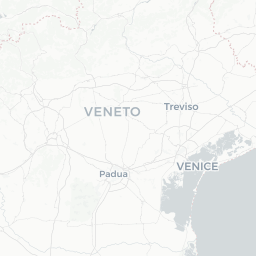
# Load the libraries
import requests
import fiona
import geopandas as gpd
from requests.auth import HTTPBasicAuth
# Define the url of the API
url = "https://www.api.automaticfarmsolutionwebapp.com/AFS/UserField?"
# Set the useremail & Password
USEREMAIL="useremail"
APIKEY="apikey"
# Set the headers for the request
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
# Make the GET request with the GeoJSON data as the request body
response = requests.get(url,
headers=headers,
auth=HTTPBasicAuth(USEREMAIL, APIKEY))
b = bytes(response.content)
with fiona.BytesCollection(b) as f:
crs = f.crs
gdf = gpd.GeoDataFrame.from_features(f, crs=crs)
# Visualize the data
gdf.explore("Zone")User data
In this part we will focus on two endpoint:
- “AFS/UserField”, This endpoint allows the user to view all the fields that have been analyzed through our service.
- “AFS/UserHectares” endpoint, This endpoint allows the user to get the analyzed area through our service
UserField
Python
In this example we will test the UserField endpoint which allow the user to get historical climate data
To use the following example you have to replace:
- USEREMAIL
- APIKEY
With your information and let’s try out the API.
R
In this example we will test the UserField endpoint which allow the user to get historical climate data
To use the following example you have to replace:
- USEREMAIL
- APIKEY
With your information and let’s try out the API.
# Import libraries
library(tictoc)
library(httr)
library(gt)
library(tidyverse)
# Define the url of the API
api_url <- "https://www.api.automaticfarmsolutionwebapp.com/AFS/UserField?"
# Set the useremail & Password
USEREMAIL="useremail"
APIKEY="apikey"
# Get the start time to API Call
tic()
# Make the GET request
r <- GET(
api_url,
httr::authenticate(
user = Sys.getenv(USEREMAIL),
password = Sys.getenv(APIKEY)
)
)
# Print out the seconds needed to create the prescription map
print("The API needed:")[1] "The API needed:"toc()1.23 sec elapsed# Get the status of the request
httr::status_code(r)[1] 200# Visulize the field boundaries
mappa <- httr::content(r, as = "text", type = "application/geo+json")
mappa<-geojsonio::geojson_sp(mappa)
mapview::mapview(mappa)Node.js
In this example we will test the UserField endpoint which allow the user to get historical climate data
To use the following example you have to replace:
- USEREMAIL
- APIKEY
With your information and let’s try out the API.
// Load Libraries
const fs = require('fs');
const axios = require('axios');
// Set the useremail & passowrd
const useremail = 'XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX';
const apikey = 'XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX';
// Set API Url
const apiEndpoint='https://www.api.automaticfarmsolutionwebapp.com/AFS/UserField?';
// Set path to save the geojson prescription map
const outputFilePath = './result.geojson';
(async () => {
try {
const authHeader = `Basic ${Buffer.from(`${useremail}:${apikey}`).toString('base64')}`;
const response = await axios.get(apiEndpoint, {
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Authorization': authHeader
}
});
const resultGeoJSON = response.data;
console.log('Answer From the API:', resultGeoJSON);
await fs.promises.writeFile(outputFilePath, JSON.stringify(resultGeoJSON, null, 2), 'utf8');
} catch (err) {
console.error('Error:', err.message);
}
})();UserHectares
Python
In this example we will test the UserHectares endpoint which allow the user to get historical climate data
To use the following example you have to replace:
- USEREMAIL
- APIKEY
With your information and let’s try out the API.
# Load the libraries
import requests
from requests.auth import HTTPBasicAuth
import pandas as pd
# Define the url of the API
url = "https://www.api.automaticfarmsolutionwebapp.com/AFS/UserHectares?"
# Set the useremail & Password
USEREMAIL="useremail"
APIKEY="apikey"
# Set the headers for the request
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
# Make the GET request
response = requests.get(url,
headers=headers,
auth=HTTPBasicAuth(USEREMAIL, APIKEY))
# Convert from response to json
data = response.json()
# Convert from json to pandas
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Let's see the first 5 agricultural products
df.head()R
In this example we will test the UserHectares endpoint which allow the user to get historical climate data
To use the following example you have to replace:
- USEREMAIL
- APIKEY
With your information and let’s try out the API.
# Import libraries
library(tictoc)
library(httr)
library(gt)
library(tidyverse)
# Define the url of the API
api_url <- "https://www.api.automaticfarmsolutionwebapp.com/AFS/UserHectares?"
# Set the useremail & Password
USEREMAIL="useremail"
APIKEY="apikey"
# Get the start time to API Call
tic()
# Make the GET request
r <- GET(
api_url,
httr::authenticate(
user = Sys.getenv(USEREMAIL),
password = Sys.getenv(APIKEY)
)
)
# Print out the seconds needed to create the prescription map
print("The API needed:")[1] "The API needed:"toc()1.14 sec elapsed# Get the status of the request
httr::status_code(r)[1] 200# Get info about the hectares
cont <- httr::content(r, as ="text", type = "application/json")
head(jsonlite::fromJSON(cont))[1] 31.0302Node.js
In this example we will test the UserHectares endpoint which allow the user to get historical climate data
To use the following example you have to replace:
- USEREMAIL
- APIKEY
With your information and let’s try out the API.
// Load Libraries
const fs = require('fs');
const axios = require('axios');
// Set the useremail & passowrd
const useremail = 'XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX';
const apikey = 'XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX';
// Set API Url
const apiEndpoint='https://www.api.automaticfarmsolutionwebapp.com/AFS/UserHectares?';
(async () => {
try {
const authHeader = `Basic ${Buffer.from(`${useremail}:${apikey}`).toString('base64')}`;
const response = await axios.get(apiEndpoint, {
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Authorization': authHeader
}
});
const resultGeoJSON = response.data;
console.log('Answer From the API:', resultGeoJSON);
} catch (err) {
console.error('Error:', err.message);
}
})();Easy - Fast - Customizable